|
Bhāskara II
Bhāskara II (c. 1114–1185), also known as Bhāskarāchārya ("Bhāskara, the teacher"), and as Bhāskara II to avoid confusion with Bhāskara I, was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. From verses, in his main work, Siddhānta Shiromani (सिद्धांतशिरोमणी), it can be inferred that he was born in 1114 in Vijjadavida (Vijjalavida) and living in the Satpuda mountain ranges of Western Ghats, believed to be the town of Patana in Chalisgaon, located in present-day Khandesh region of Maharashtra by scholars. He is the only ancient mathematician who has been immortalized on a monument. In a temple in Maharashtra, an inscription supposedly created by his grandson Changadeva, lists Bhaskaracharya's ancestral lineage for several generations before him as well as two generations after him. Colebrooke who was the first European to translate (1817) Bhaskaracharya II's mathematical classics refers to the family as Maharashtrian Brahmins residing on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
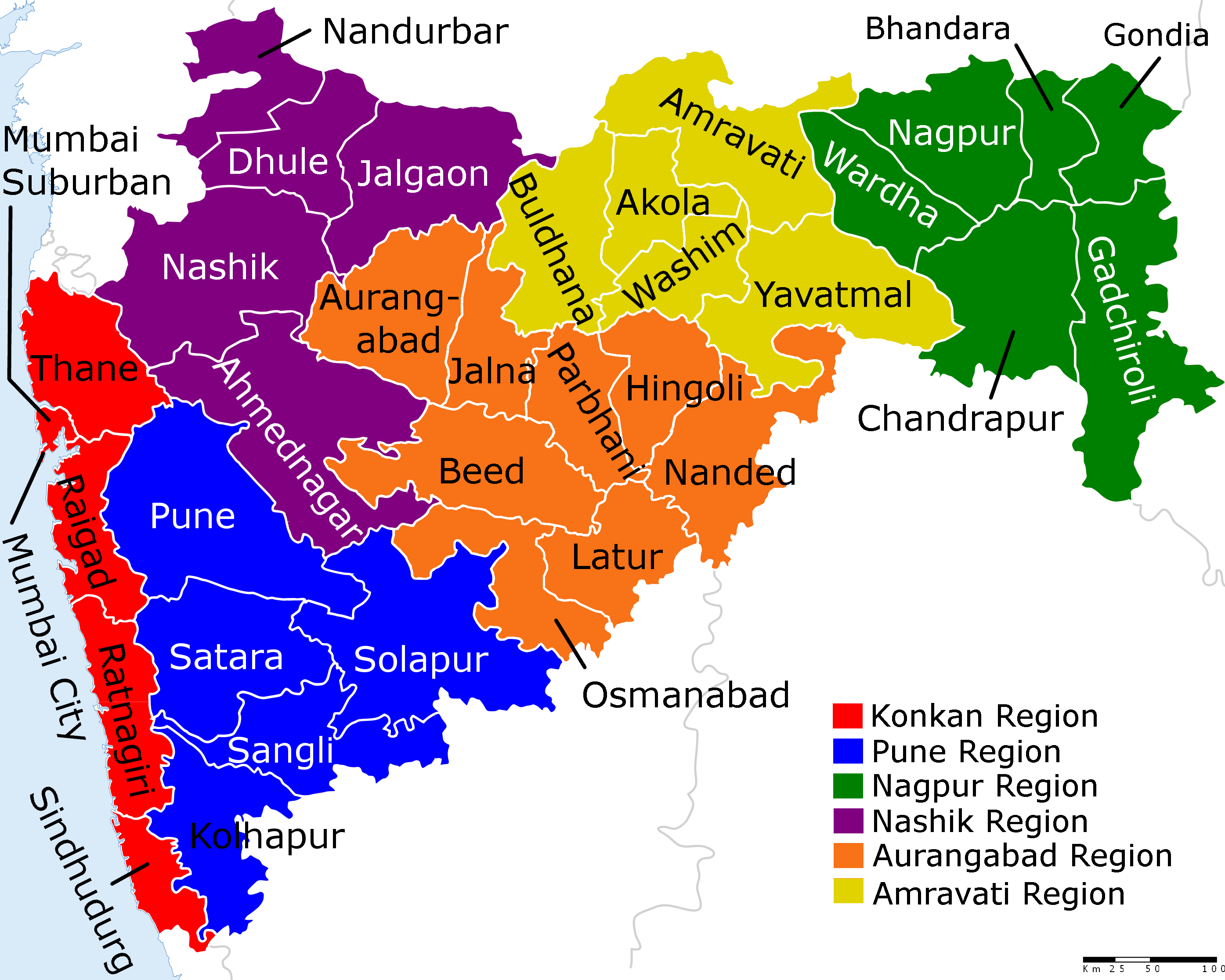
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union territories of India by population, second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdivision globally. It was formed on 1 May 1960 by splitting the bilingual Bombay State, which had existed since 1956, into majority Marathi language, Marathi-speaking Maharashtra and Gujarati language, Gujarati-speaking Gujarat. Maharashtra is home to the Marathi people, the predominant ethno-linguistic group, who speak the Marathi language, Marathi language, the official language of the state. The state is divided into 6 Divisions of Maharashtra, divisions and 36 List of districts of Maharashtra, districts, with the state capital being Mumbai, the List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, most populous urban area in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian People
Indians or Indian people are the Indian nationality law, citizens and nationals of India. In 2022, the population of India stood at over 1.4 billion people, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous country, containing 17.7 percent of the global population. In addition to the Indian population, the Non-resident Indian and Overseas Citizen of India, Indian overseas diaspora also boasts large numbers, particularly in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf and the Western world. While the demonym "Indian" applies to people originating from the present-day Republic of India, it was also formerly used as the identifying term for people originating from Pakistan and Bangladesh during British Raj, British colonial era until 1947. Particularly in North America, the terms "Asian Indian" and "East Indian" are sometimes used to differentiate Indians from the indigenous peoples of the Americas; although the Native American name controversy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munishvara
Munishvara or Munīśvara Viśvarūpa (born 1603) was an Indian mathematician who wrote several commentaries including one on astronomy ''Siddhanta Sarvabhauma'' (1646) which included descriptions of astronomical instruments such as the ''pratoda yantra''. Another commentary was ''Lilavativivruti''. Very little is known about his other than that he came from a family of astronomers including his father Ranganatha who wrote a commentary called ''Gụ̄hārthaprakaśa/Gūḍhārthaprakāśikā,'' a commentary on the '' Suryasiddhanta''. His grandfather Ballala had his origins in Dadhigrama in Vidharba and had moved to Benares and several sons wrote commentaries on astronomy and mathematics. Munisvara's ''Siddhantasarvabhauma'' had the patronage of Shah Jahan like his paternal uncle Krishna Daivagna. He was opposed to fellow mathematician Kamalakara whose brother also wrote a critique of Munisvara's bhangi-vibhangi method for planetary motions. He was also opposed to the adoption of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahāvīra (mathematician)
Mahāvīra (or Mahaviracharya, "Mahavira the Teacher") was a 9th-century Jain mathematician possibly born in Mysore, in India. He authored '' Gaṇitasārasan̄graha'' (''Ganita Sara Sangraha'') or the Compendium on the gist of Mathematics in 850 AD. He was patronised by the Rashtrakuta king Amoghavarsha. He separated astrology from mathematics. It is the earliest Indian text entirely devoted to mathematics. He expounded on the same subjects on which Aryabhata and Brahmagupta contended, but he expressed them more clearly. His work is a highly syncopated approach to algebra and the emphasis in much of his text is on developing the techniques necessary to solve algebraic problems. He is highly respected among Indian mathematicians, because of his establishment of terminology for concepts such as equilateral, and isosceles triangle; rhombus; circle and semicircle. Mahāvīra's eminence spread throughout South India and his books proved inspirational to other mathematicians in Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sridhara
Śrīdhara, Śrīdharācāryya or Śrīdhara Acharya ( 870 CE – 930 CE) was an Indian mathematician, Sanskrit pandit and philosopher. He was born in Bhuriśreṣṭi (Bhurisriṣṭi or Bhurśuṭ) village in South Rādha at present day Hugli in West Bengal, then undivided Bengal with its Capital at Gaur. His father's name was Baladevācārya or Baladeva Acharya and his mother's name was Acchoka Devi. His father was a Sanskrit pandit and philosopher. Notable books He is known for two main treatises: Trisatika (300) (sometimes called the Patiganitasara ) and the Pāṭīgaṇita ( bn, পাটীগণিত). It was written in three hundred ''ślokas'' thus his major work Pāṭīgaṇitasāra was named Triśatika. The book discusses counting of numbers, natural number, zero, measures, multiplication, fraction, division, squares, cubes, rule of three, interest-calculation, joint business or partnership, and mensuration (the main part of geometry concerned with ascertai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established doctrine of Brahma", dated 628), a theoretical treatise, and the '' Khaṇḍakhādyaka'' ("edible bite", dated 665), a more practical text. Brahmagupta was the first to give rules for computing with ''zero''. The texts composed by Brahmagupta were in elliptic verse in Sanskrit, as was common practice in Indian mathematics. As no proofs are given, it is not known how Brahmagupta's results were derived. In 628 CE, Brahmagupta first described gravity as an attractive force, and used the term "gurutvākarṣaṇam (गुरुत्वाकर्षणम्)" in Sanskrit to describe it. Life and career Brahmagupta was born in 598 CE according to his own statement. He lived in ''Bhillamāla'' in Gurjaradesa (modern Bhinmal in Rajasthan, India) during the reign of the Chavda dynasty ruler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Āryā Metre
''Āryā meter'' is a meter used in Sanskrit, Prakrit and Marathi verses. A verse in metre is in four metrical lines called ''pāda''s. Unlike the majority of meters employed in classical Sanskrit, the meter is based on the number of s (morae) per . A short syllable counts for one , and a long syllable (that is, one containing a long vowel, or a short vowel followed by two consonants) counts for two s. It is believed that meter was taken from the gatha meter of Prakrit. metre is common in Jain Prakrit texts and hence considered as favourite metre of early authors of Jainism. The earlier form of the metre is called old , which occurs in a some very early Prakrit and Pàli texts. Āryā The basic verse has 12, 18, 12 and 15 s in the first, second, third, and fourth ''pāda''s respectively. An example is the following from Kālidāsa's play '' Abhijñānaśākuntalam'' (c. 400 CE): : : : : : : : – u u , – – , u u – : u – u , – – , u – u , – – , � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deshastha Brahmin
Deshastha Brahmin is a Hindu Brahmin subcaste mainly from the Indian state of Maharashtra and northern area of the state of Karnataka. Other than these states, according to authors K. S. Singh, Gregory Naik and Pran Nath Chopra, Deshastha Brahmins are also concentrated in the states of Telangana , Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh Author Pran Nath Chopra and journalist Pritish Nandy says, "Most of the well-known saints from Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh were Deshastha Brahmins". The mother tongue of Deshastha Brahmins is either Marathi or Kannada. Some Deshasthas who settled in Telugu states also adopted Telugu as their mother tongue. Over the millennia, the Deshastha community has produced Mathematicians such as Bhāskara II, Sanskrit scholars such as Bhavabhuti; Bhakti saints such as Dnyaneshwar, Sripadaraja, Eknath, Purandara Dasa, Samarth Ramdas and Vijaya Dasa; Logicians such as Jayatirtha and Vyasatirtha. The traditional occupation of Deshastha Brahmins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godavari River
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It flows east for , draining the states of Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of tributaries. Measuring up to , it forms one of the largest river basins in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin. In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been dubbed as the Dakshina Ganga (Ganges of the South). The river has been revered in Hindu scriptures for many millennia and continues to harbour and nourish a rich cultural heritage. In the past few decades, the riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtrian Brahmin
Marathi Brahmins (also known as Maharashtrian Brahmins), are communities native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. They are classified into mainly three sub-divisions based on their places of origin, " Desh", "Karad" and "Konkan". The Brahmin subcastes that come under Maharashtra Brahmins include Deshastha, Chitpavan (Konkanastha), Saraswat, Karhade, and Devrukhe. Geographical distribution Maharashtrian Brahmins are native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. However, their training as priests, expertise in Hindu laws and scriptures, and administrative skills have historically led them to find employment in all corners of India. For example, in the 1700s, the court of Jaipur had Maharashtrian Brahmins recruited from Benares. This community had in turn migrated to Benares after the fall of Vijayanagar empire in southern India. The greatest movement of the community took place when the Maratha Empire expanded across India. Peshwa, Holkars, Scindia, and Gaekwad dynastic leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |